
In Linux we have with different tools with which we can manage our hard drives and their partitions, each with something that characterizes it from the others, we have easy to use administrators thanks to the fact that they have a user interface (GUI) and others that tend to be a bit more complicated to use since they are handled from the terminal.
This time we are going to review some of the best partition managers that we can find in Linux.
Before mentioning these, I would like to make a small and important comment:
The handling of the following tools has a certain degree of risk, due to the capacity they have of handling the hard disk, you can lose important information if you do not know how to handle them. That is why I recommend that you perform your tests of these on a virtual machine.
Since if you do it on your hard drive, you run a risk if you make a mistake, That said, it is your decision how you use them.
We will start with one of the best known partition managers that has a graphical interface, the first in this list is:
Gparted

GParted is a partition editor for the GNOME desktop environment. This application is used to create, delete, resize, inspect and copy partitions, as well as the file systems found on them. This is useful to create space for new operating systems, rearrange disk usage and create disk images on a partition.
It has a fairly intuitive interface, in which we can manage the partitions or hard drives from the main menu of the application or with the use of the secondary click on the desired partition or disk to modify.
This administrator found in most Linux distributions, since it is part of the Gnome project.
gnome disks
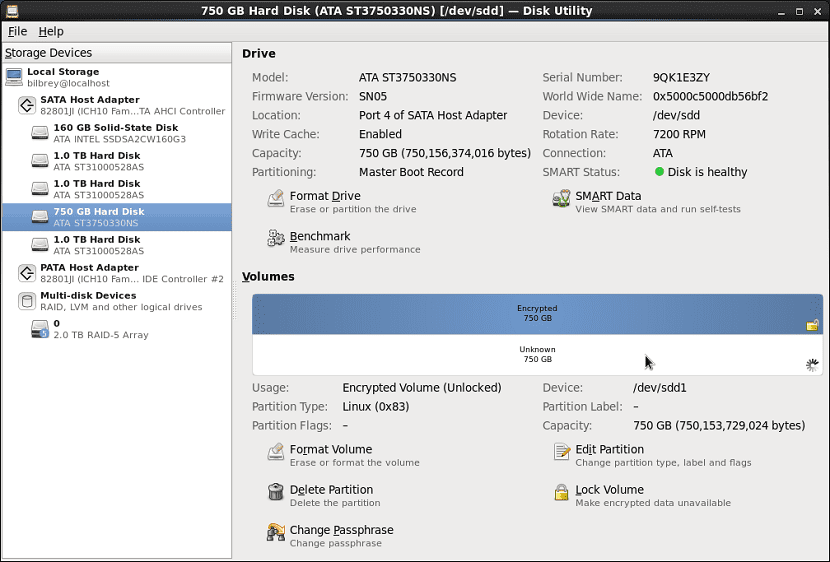
What Gnome Disks is a graphical front-end of udisks included in the gnome-disk-utility package this is another partition editor that belongs to the Gnome project.
With her partition management can be doneFor those who are migrating or are Windows users, they have probably used Crystal Disk, well, Gnome disk will be somewhat familiar to them. It also allows us SMART type motorization, benchmarking and software RAID
This tool is quite popular since it can be found as the default tool on various Linux distributions including Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Trisquel, Fedora, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 63, and CentOS.
KDE Partition Manager

This is a partition editor, which makes use of the GNU Parted library, to allow the user to manage partitions, of which the tasks it allows to perform we find the following:
Create, delete, check, resize and copy partitions and the file systems on them.
This is useful for creating space on a disk for new operating systems, reorganize disk usage, copy data that was on a hard disk and make a "mirror copy" from one partition to another. Additionally, KDE Partition Manager can back up file systems and restore those copies.
Fdisk

This is another of the many most popular partition managers in Linux, Fdisk is included in most Linux distributions and it is usually the tool of this type most used by users.
Fdisk allows the user to do what any partition manager can do, what makes Fdisk special is that it is not an exclusive tool for Linux, but it is cross-platform.
Fdisk part of util-linux-ng and allows us to create partitions on 94 different file systems, including FAT32, Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, Solaris, and QNX. Fdisk does not have a graphical interface, so its use is based on the command line.
cfdisk
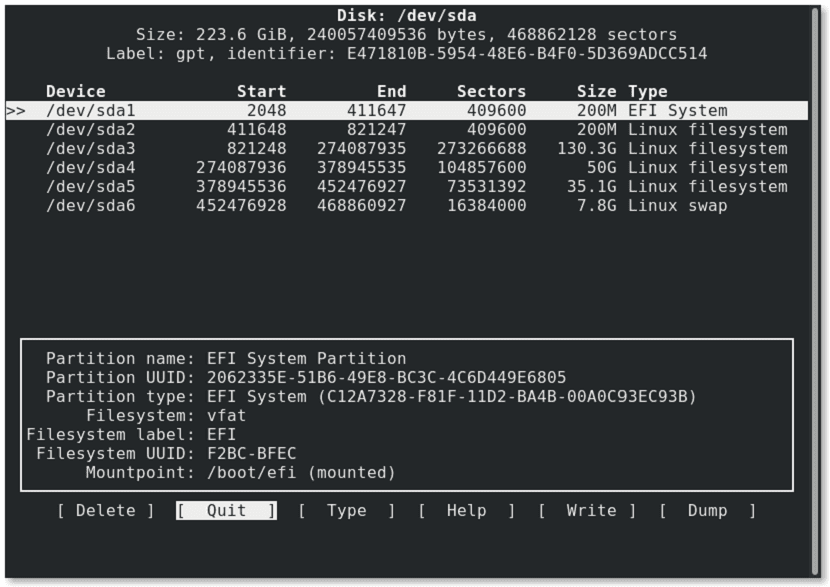
Es a partition editor similar to fdisk, since its use is also through the command line, but with a different interface than fdisk, cfdisk tries to read partition tables from disk, showing found ones.
The current cfdisk implementation relies on libfdisk and supports master boot record, GUID partition table, BSD disk label, SGI and SUN disk labels. As well provides information about the contents of the partitions.