A group of researchers at Tsinghua University (Chinese) has developed a technique for listening to conversations in a room containing an optical cable, for example, used to connect to the Internet.
Sound vibrations create pressure drops in the air, so microvibrations are produced in the optical cable, modulated with a light wave transmitted through the cable. The resulting distortions can be analyzed over a sufficiently large distance using a Mach-Zehnder laser interferometer.
In recent years, fiber optic networks are widely deployed around the world, which not only facilitates data transmission, but also provides an opportunity to obtain additional information.
These applications of fiber optic networks, including earthquake detection, urban traffic flow monitoring [7-10], exploration of underground geological structures, etc., have positive impacts on production and people's lives. However, it also brings some potential security issues, which should be carefully considered.
During the experiment, it was possible to fully recognize the sound of speech in the presence of an open piece of optical cable (FTTH) three meters in front of the modem.
The measurement was made at a distance of 1,1 km from the end of the cable located in the listening room. Listening range and the ability to filter out interference correlates with the length of the cable in the room, that is, as the length of the cable in the room decreases, the maximum distance from which it is possible to listen also decreases.
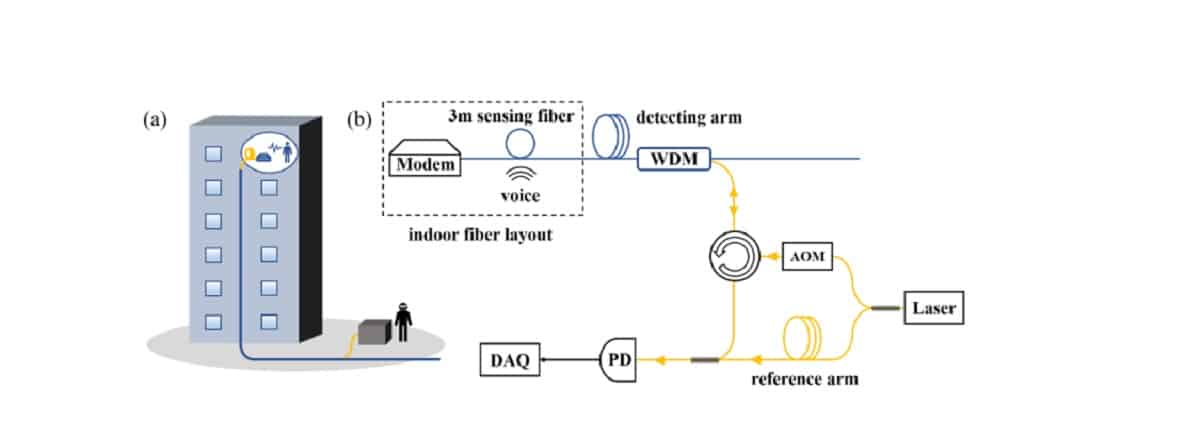
It is shown that the detection and restoration of an audio signal in optical communication networks it can be implemented covertly, unnoticeable to the listener and without violating the communication functions used. To slip discreetly into the communication channel, the researchers used a division multiplexer of wavelength (WDM, Wavelength Division Multiplexer). Further reduction of the background noise level is achieved by balancing the arms of the interferometer.
Optical fibers are sensitive to variations in ambient pressure, which could be induced
by acoustic waves. Devices based on this feature are widely used in sound detection, such as fiber optic hydrophones. Based on the current fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployment mode, tail fiber up to several meters will be installed in residents' homes. For these internal fibers, the sound signals could be modulated on the light wave transmitted therein, allowing others to eavesdrop and retrieve them at remote locations along the fiber link.
Meanwhile, the original communication function of fiber will not be affected by the use of wavelength division multiplexer (WDM). Therefore, eavesdropping can be carried out secretly. In this article, we propose an espionage scheme using indoor fiber optics and
prove it in the lab. The system is based on the Mach-Zehnder heterodyne
interferometer. We coupled the listening system to the 1,1 kilometer fiber optic link
away from the listening target, the voices of normal human speech (50 ~ 80 dB) can be
eavesdropped with a 3 meter indoor tail fiber. System noise and eavesdropping capabilities are analyzed. Finally, we discuss measures to avoid the risk of illegal eavesdropping.
countermeasures clandestine eavesdropping include reducing the length of the optical cable in the room and lay the cable in rigid cable channels. You can also use APC optical connectors (Angled Physical Connection) angled instead of flat end connectors (PC) to reduce hearing efficiency. For fiber optic cable manufacturers, it is recommended to use materials with a high modulus of elasticity, such as metal and glass, as the fiber cladding.
Finally, for those who are interested in knowing more about it, they can consult the details of the investigation In the following link.